Courtesy & Copyright Hilary Shughart, Photographer
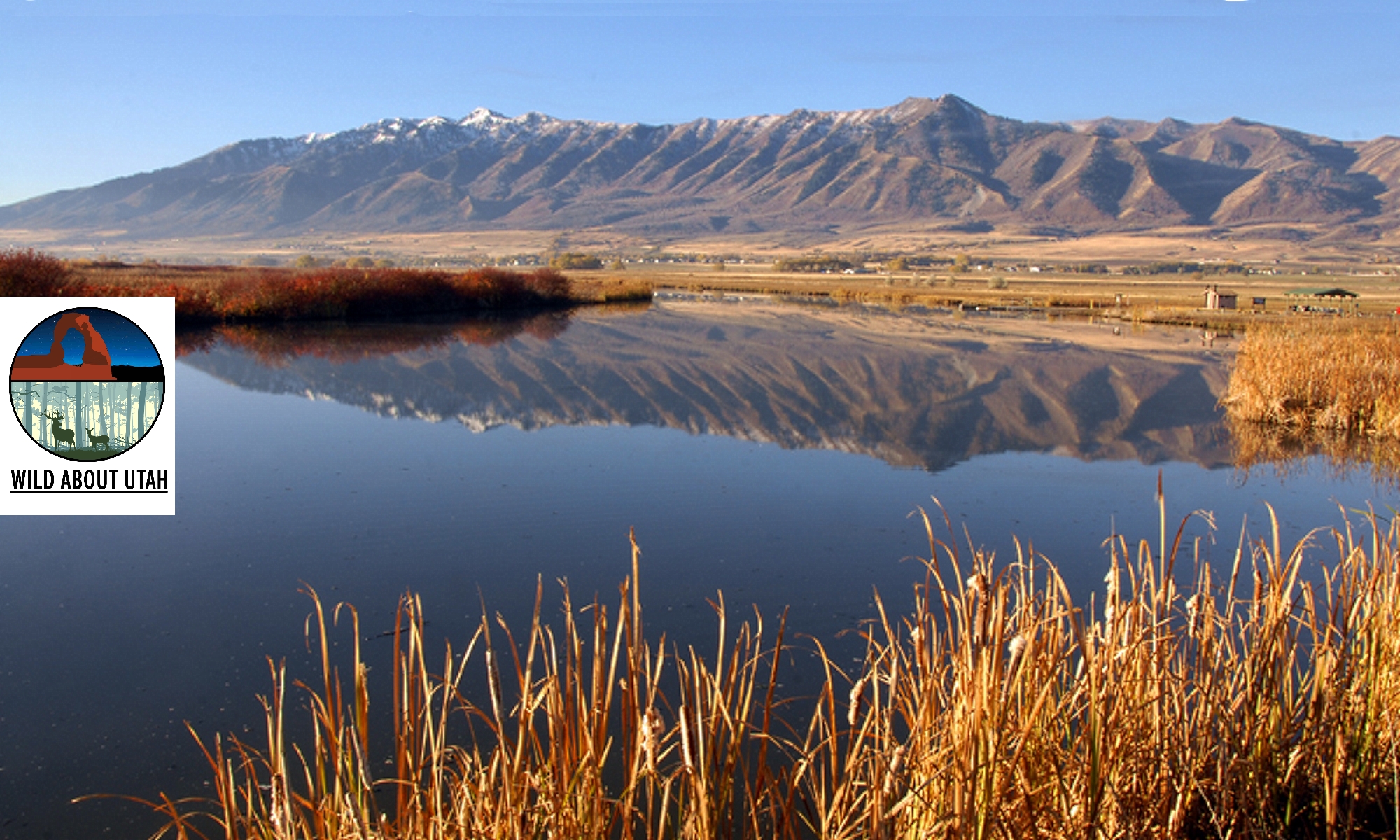
Throughout history, cities and towns have often been established along the banks of rivers, because these waterways provide a source of drinking water, power, and transport links to other communities. The City of Logan, Utah, is no exception – in fact it was just over a century and a half ago, in the Spring of 1859, when the first white settlers chose to camp on the banks of the Little Logan River in what is now named Merlin Olsen Central Park. Right away, they began building mills and farming the fertile Island between the rivers. Our natural and cultural heritage are linked to water, so it’s an exciting opportunity to be inspired by the PBS KIDS Utah Writers & Illustrators Contest theme of “Our Water, Our Future”. Children in Kindergarten-6th Grade are invited to participate, and stories are accepted in English and Spanish, can be fiction or nonfiction, may be about your very own neighborhood or faraway lands. Anyone can take a look at the PBS Utah activity sheets and printable resources online.
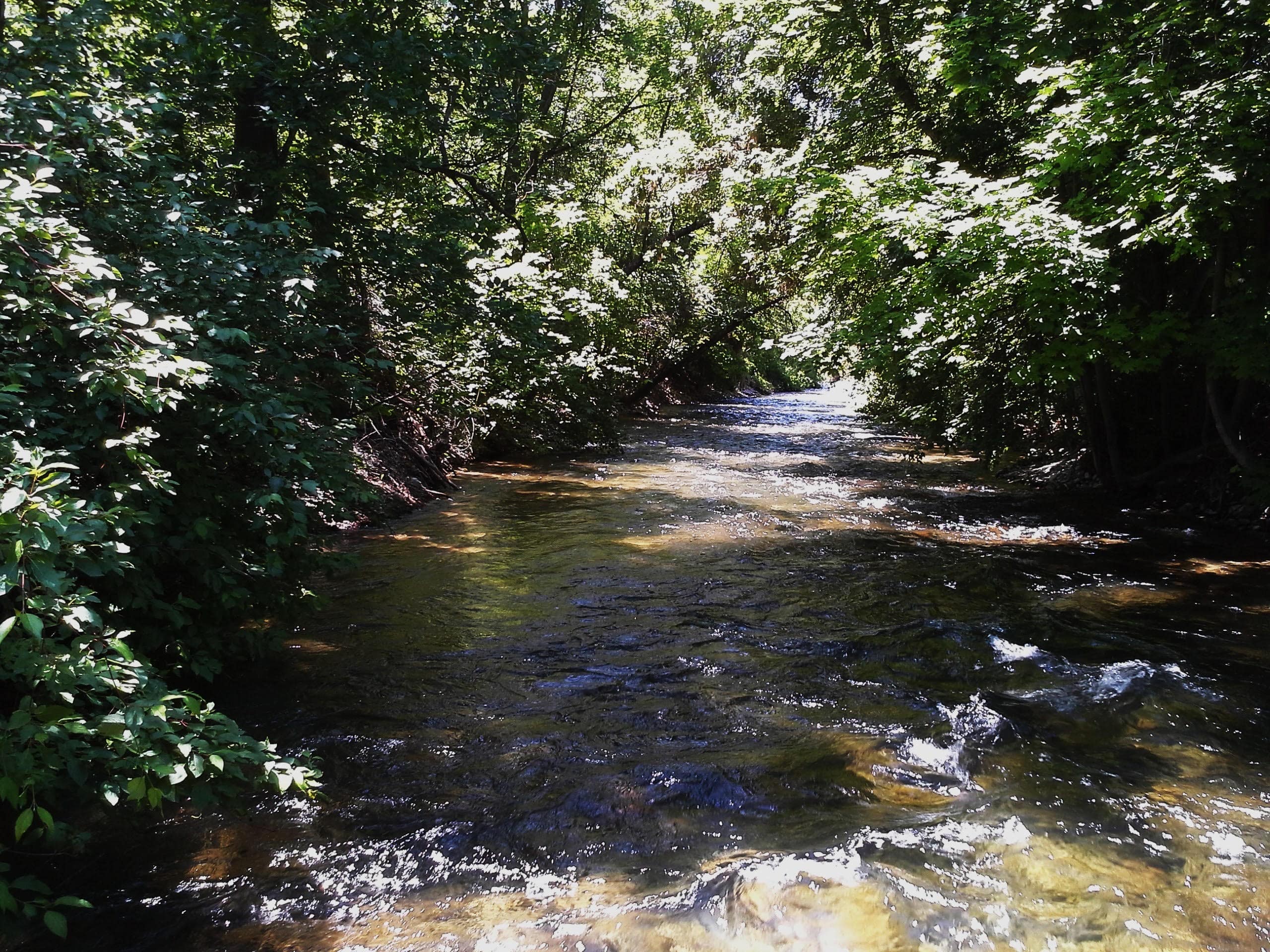
Do you have a favorite neighborhood park where you go wading and tubing? Did you know that the Little Logan River flows through half a dozen beloved parks, including River Hollow Park which was established at the source, where the Little Logan River branches north from the Logan River. The Little Logan meanders through town where it used to power multiple mills, including Central Mills, established in 1867 and considered to be the oldest continuously-run business in the state. The river is an anabranch of the Logan River, a diverging branch of the river which re enters the main stream at the west edge of town. Fun Fact: In Australian Public Works Departments* an anabranch is called a billabong!
Speaking of water, if you put a shallow bowl of clean water out for birds you might see them flock to your little oasis for a drink and a careful Tai Chi-like bathing ritual, and with a heated bird bath in winter, you might witness a fascinating meeting of a variety of species gathering around the warm watering hole, perhaps sharing a quiet appreciation for the nutritious seeds in the nearby dried Sunflowers, Black-eyed Susans, and Indian Rice Grass.
Hearing the birds brings to mind the insightful observations by Terry Tempest Williams, that “Once upon a time, when women were birds, there was the simple understanding that to sing at dawn and to sing at dusk was to heal the world through joy. The birds still remember what we have forgotten, that the world is meant to be celebrated.”
Now is the time to celebrate the biodiversity supported by our rivers and lakes, and each and every life-sustaining drop of water in our watersheds.
I’m Hilary Shughart with the Bridgerland Audubon Society, and I am Wild About Utah!
Credits:
Images: Courtesy & Copyright, Hilary Shughart, Photographer
Featured Audio: Courtesy & Copyright © Kevin Colver, https://wildstore.wildsanctuary.com/collections/special-collections/kevin-colver AND Friend Weller, Retiring Engineer, Utah Public Radio, https://www.upr.org/people/friend-weller
Text: Hilary Shughart, President, https://bridgerlandaudubon.org/
Additional Reading: Hilary Shughart and Lyle Bingham, https://bridgerlandaudubon.org/
Additional Reading
WildAboutUtah pieces by Hilary Shughart, https://wildaboututah.org/author/hilary-shughart/
Full Power Flour: The relationship between the farmer, the miller and the baker are key to the success of Central Milling’s organic mission. By Darby Doyle https://www.visitutah.com/Articles/Full-Power-Flour
Little Logan River Topo Map https://www.topozone.com/utah/cache-ut/stream/little-logan-river/
An anabranch is a channel of water that leaves a river or stream and then rejoins again further downstream. An anabranch is considered to be part of the river or stream that it comes from.
An anabranch can be nearly half of a river’s flow of water. When there is an island in the river, an anabranch is created as water passes around the island. The smaller channel of water passing the island is an anabranch of the river. http://worldlandforms.com/landforms/anabranch/
PBS KIDS Utah Writers & Illustrators Contest: Our Water, Our Future https://www.pbsutah.org/kids/writers-illustrators-contest/?utm_source=sfmc&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=03.21.24+E-news&utm_term=https%3a%2f%2fwww.pbsutah.org%2fkids%2fwriters-illustrators-contest%2f&utm_id=114875&sfmc_id=147746441
“Unlike Main Street, or Center Street, or 400 North Street, which are streets of commerce, the Little Logan River is the raison d’etre of the City of Logan. “
A History of Logan Island, by Virginia C. Parker, Logan, Utah, 2007, http://exhibits.usu.edu/exhibits/show/the-island-market/item/25944
Billabong https://cide.en-academic.com/dic.nsf/cide/17968/Billabong
Working Water in Cache Valley, Cache Pioneer Museum, Cache Chapter of the Daughters of the Utah Pioneers, https://cachedupmuseum.org/in-the-news.html
Terry Tempest Williams, When Women Were Birds: Fifty-four Variations on Voice, Sarah Crichton Books; First Edition (April 10, 2012) https://www.amazon.com/When-Women-Were-Birds-Fifty-four/dp/1250024110
ECONET April 2, Proposal to sever the Little Logan River from the Logan River, 5:30 p.m. Logan City Hall, 290 N 100 West Logan, UT, Bridgerland Audubon Society, March 29, 2024, https://bridgerlandaudubon.org/econet-proposal-to-sever-little-logan-river-from-logan-river/