Courtesy Pixabay, Filio (Tom) contributor
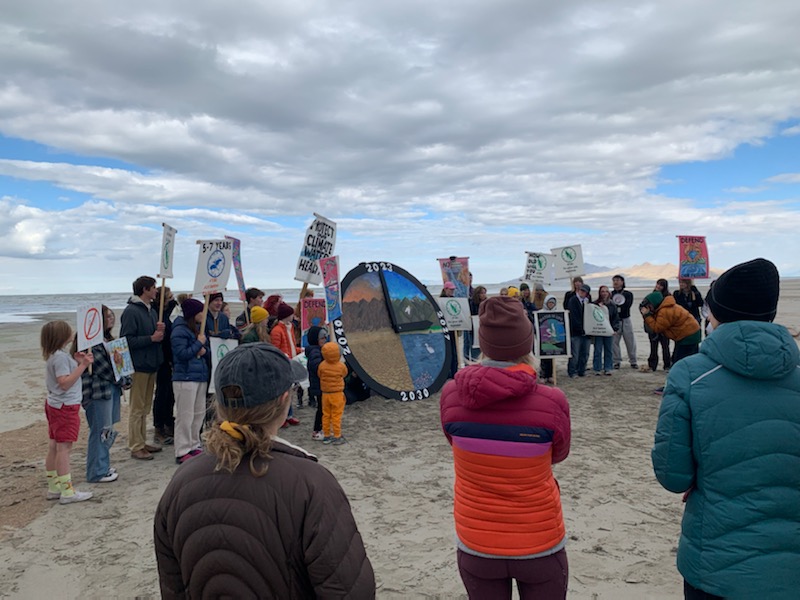 Great Salt Lake Countdown Clock
Great Salt Lake Countdown Clock
Courtesy & © Jack Greene, photographer
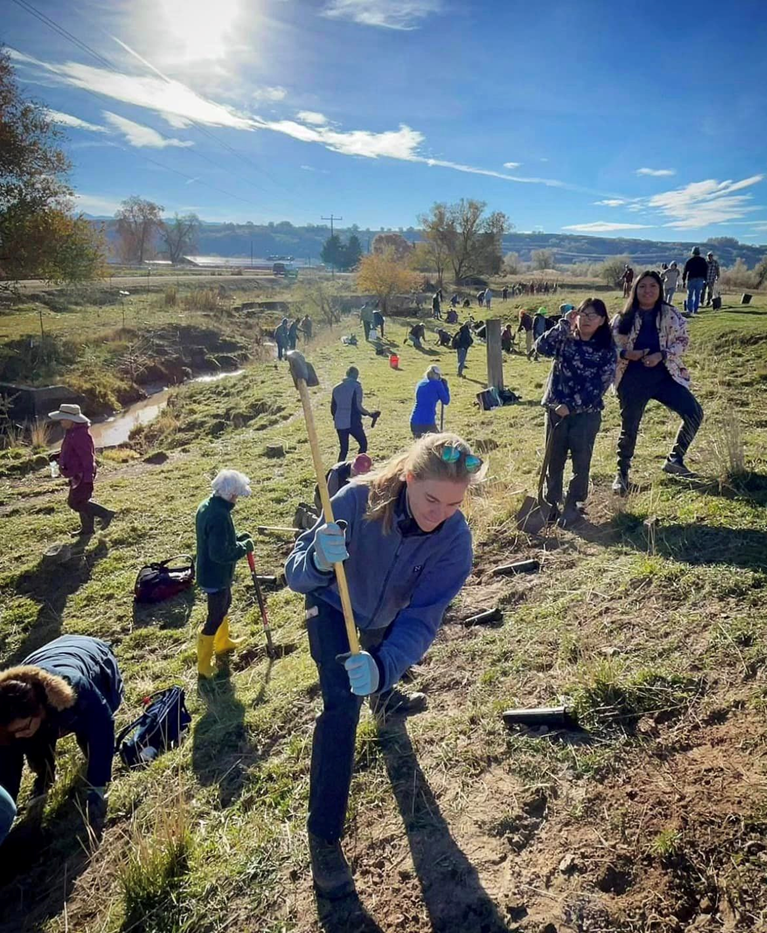
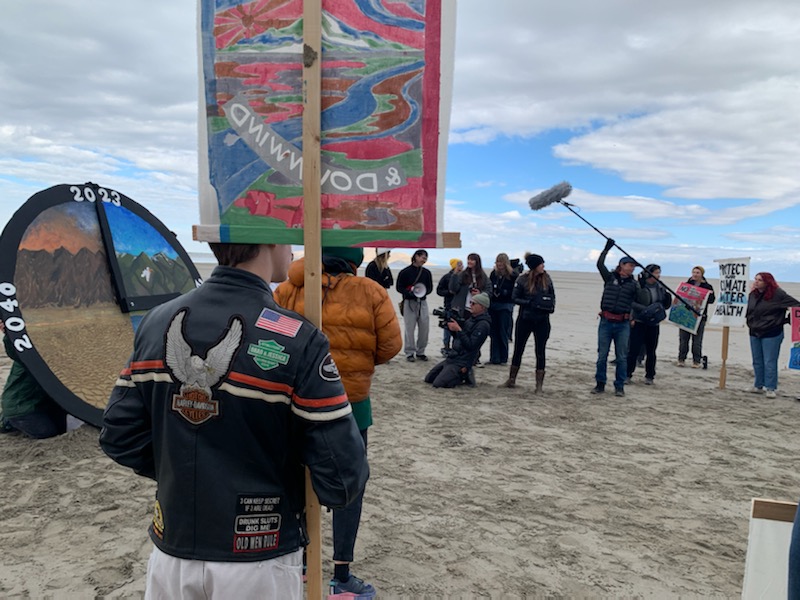 Utah Youth Environmental Solutions (UYES)
Utah Youth Environmental Solutions (UYES)
Great Salt Lake Countdown Clock
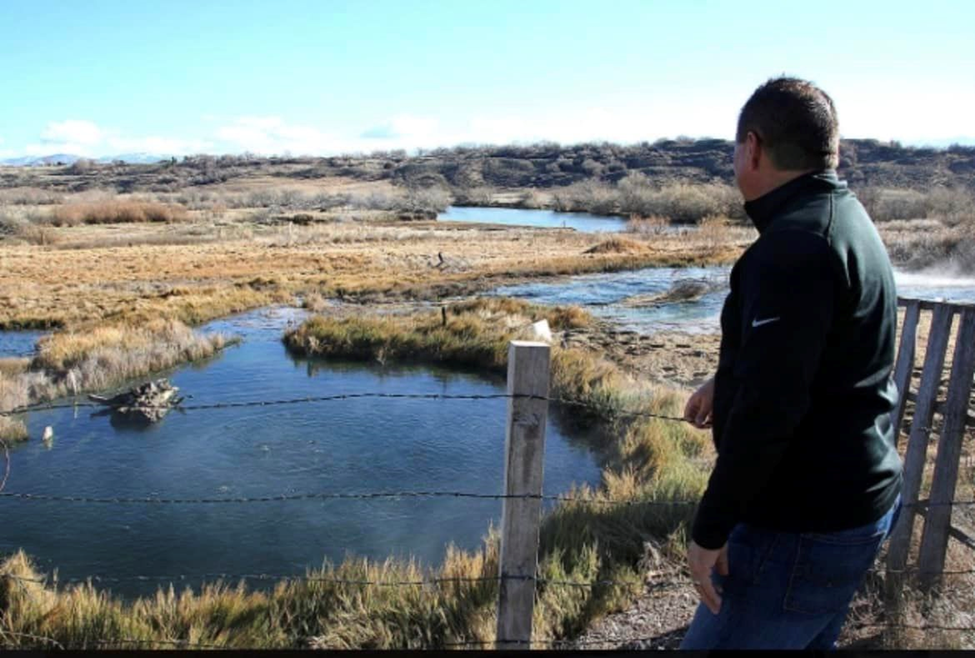
Courtesy & © Jack Greene, photographer
 Great Salt Lake Countdown Clock
Great Salt Lake Countdown Clock
Courtesy & © Jack Greene, photographer
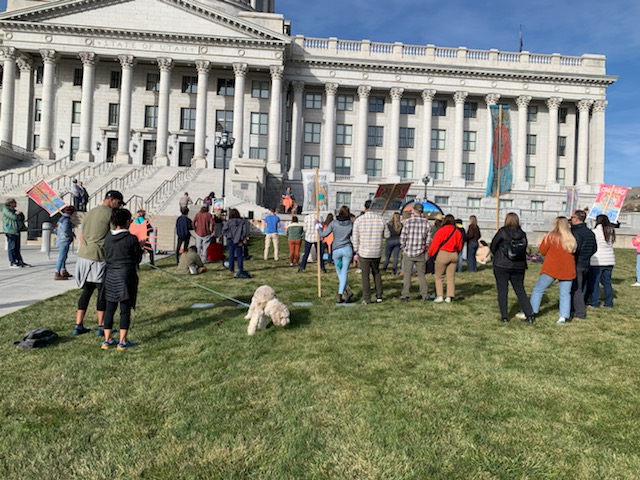 Native and Youth Voices Honoring the Great Salt Lake Event November 11, 2023
Native and Youth Voices Honoring the Great Salt Lake Event November 11, 2023
Courtesy & © Jack Greene, photographer
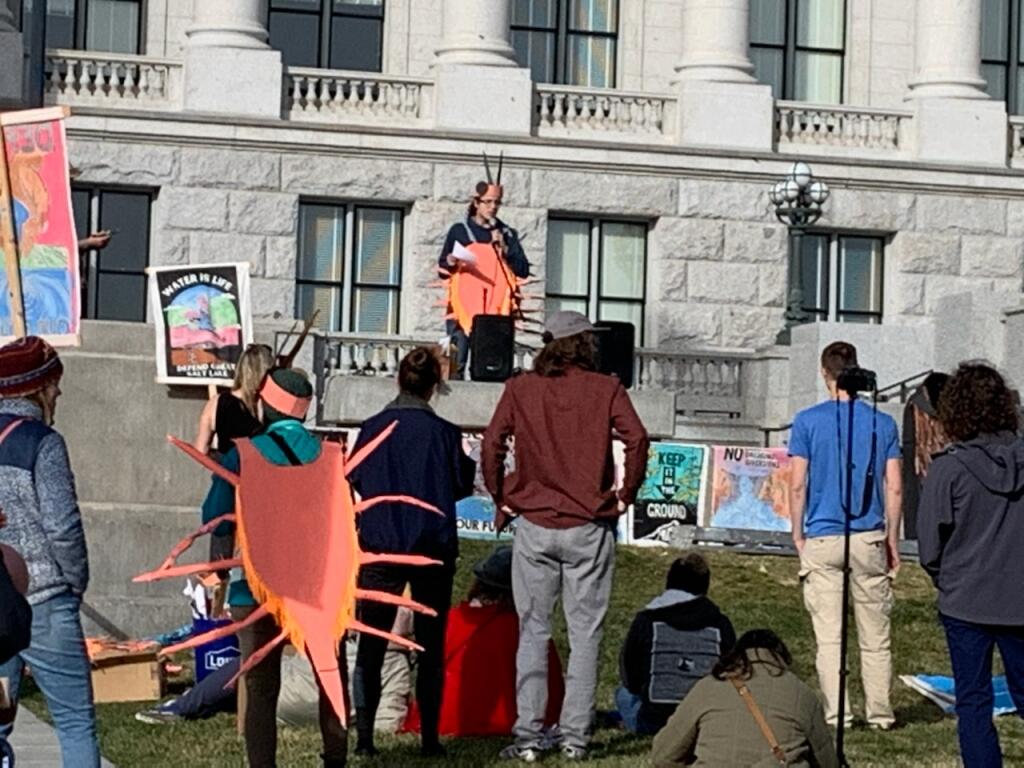 Brine Shrimp Art at the Native and Youth Voices Honoring the Great Salt Lake Event November 11, 2023
Brine Shrimp Art at the Native and Youth Voices Honoring the Great Salt Lake Event November 11, 2023
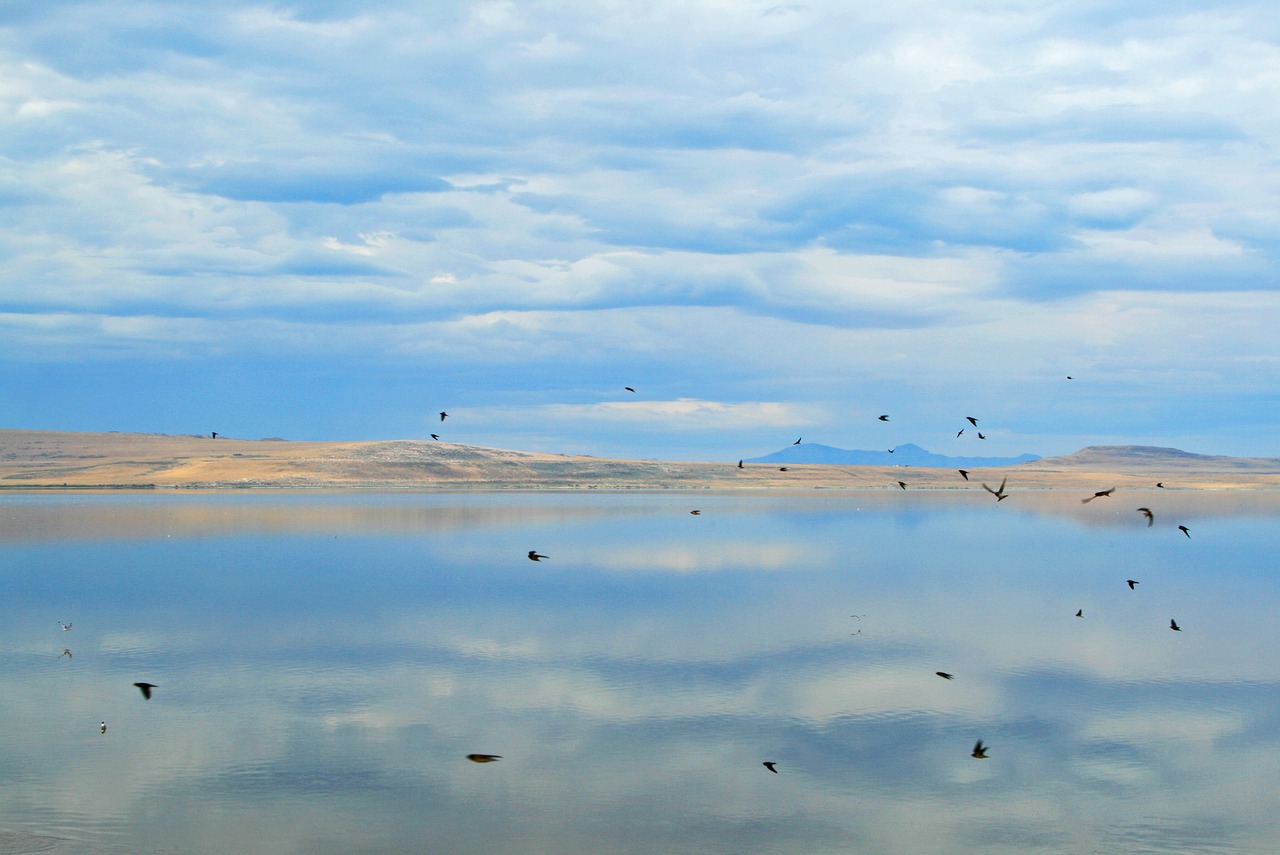
Courtesy & © Jack Greene, photographerOn October 28th, we gathered near the Salt Aire on the north shore of the Great Salt Lake. A sharp, cold wind kept us huddled. We walked nearly a half mile of mud flats on a path strewn with eared grebe carcasses to reach our destination, a giant, 7-foot clock. The clock displayed four different scenarios of our future based on various lake levels. At the 12 O’clock hour was 4200’, the ideal lake level for healthy waters to support brine shrimp, brine flies, and microbialites, all essential for the millions of birds that feast on them; and to cover the toxic dusts generated by a dry lake bed.
A youth driven event, they poured out their hearts and deep concerns with eloquent testimony for the lake’s diminished health, which translated to their health. The dead grebes were a grim reminder of what the lake has become from the Jordan, Weber, and especially the Bear River being diverted to serve human demands.
Two weeks later, a mixed assemblage of Native and youth gathered on our state capitol steps accompanied by Making Waves for the Great Salt Lake human sized brine shrimp puppets, musicians, and a phalarope dancing to exquisite poetry, to deliver their offerings honoring the Lake. Several tribal members, including Shoshone and Goshute, shared stories of their deep history and cultural connections. Youth representing the Utah Youth for Environmental Solutions and the Great Salt Lake Youth Coalition offered soul piercing words.
Two Saturday’s ago, I entered Westminster University Gore Hall greeted by youth, artists, organizations, and many seniors. Brine shrimp, brine fly, eared grebes, avocets and California gull puppets decorated walls and tables, representing a few of the hundreds of species that call the Great Salt Lake home, or a nice stopover as they wing their way around the globe.
The 4-hour youth led event was hosted by the Westminster Great Salt Lake Institute and lead by several youth organizations and various supporting groups. Many had attended our rally on the capitol steps. This amalgam of intergenerational individuals working on behalf of saving the Great Salt Lake ecosystem was heartening, and essential for the lake to continue on.
We were trained on how best to effect good policy with our Utah legislators through building positive relationships and preparing well researched and documented information to educate them on our interests. Another Rally is planned for Saturday, January 20th at 3 pm on the south steps of the Capitol. Many voices will be heard, including Ute tribal member Forest Cuche, many youth, and Utah author, Terry Tempest Williams.
Looking ahead, Salt Lake City may once again host the winter Olympics in 2034. May our internationally renowned Great Salt Lake be present to welcome them, and may our snow be white and bright, not brown and gone, from a covering of dust blown from an empty lake bed.
A few Secret Santa Ideas for the Great Salt Lake: write, text, or call your elected officials; make art about the lake and post it on social media; Perhaps most important, enjoy the many gifts our Great Lake offers, especially the millions of wings that grace our heavens!
Jack Greene for Bridgerland Audubon Society, and I’m wild about our wild and wonderful Great Lake!
Credits:
Images: Jack Greene, Bridgerland Audubon, https://bridgerlandaudubon.org/
Audio: Courtesy & © Kevin Colver, https://wildstore.wildsanctuary.com/collections/special-collections
Text: Jack Greene, Bridgerland Audubon, https://bridgerlandaudubon.org/
Additional Reading: Lyle Bingham and Jack Greene, Author, Bridgerland Audubon, https://bridgerlandaudubon.org/
Additional Reading:
Jack Greene’s Postings on Wild About Utah, https://wildaboututah.org/author/jack/
McCormick, John S., Saltair, Utah History Encyclopedia, 1994, Utah Division of State History, Utah Department of Cultural and Community Engagement, https://historytogo.utah.gov/saltair/
Utah youth march with giant clock in support of Great Salt Lake bill, ABC4-TV, Oct 28, 2023
Join the Vigil for Great Salt Lake, happening EVERY DAY of the 2024 Legislative Session at the Utah State Capitol from 8-9 am and 5-6 pm:
Great Salt Lake 2024 Daily Vigil, Walk with the Waves 8-9 am, Tue Jan 16, 2024 – Fri Mar 1, 2024, Making Waves for Great Salt Lake Artist Collaborative, https://signup.com/client/invitation2/secure/113888296054/false#/invitation
Celebrate the Lake Species! 5-6 pm, Tue Jan 16, 2024 – Fri Mar 1, 2024, Making Waves for Great Salt Lake Artist Collaborative, https://signup.com/client/invitation2/secure/82319992083/false#/invitation
Making Waves for Great Salt Lake Artist Collaborative, https://sarahlizmay.com/making-waves-for-great-salt-lake-artist-collaborative
Lake Art from the Making Waves for Great Salt Lake Artist Collaborative, Supported in part by Great Salt Lake Audubon and Bridgerland Audubon, https://bridgerlandaudubon.org/lake-art-puppets/
Utah Youth Environmental Solutions (UYES), https://utahyes.org/
Write to your legislators: https://le.utah.gov/GIS/findDistrict.jsp
Grow the Flow, Conserve Utah Valley, https://growtheflowutah.org/
- Secret Santa for Great Salt Lake (Courtesy Nathan Thompson, GrowTheFlowUtah.org, Dec 12, 2023)
- Invite someone new to get involved with helping Great Salt Lake
- Donate to an organization working to save Great Salt Lake
- Write to your elected officials about Great Salt Lake
- Express gratitude for the lake in prayer and/or conversation
- Make art about the lake and post it on social media
- Turn off sprinklers
- Contact local churches or other organizations about decreasing turf in public/shared spaces





